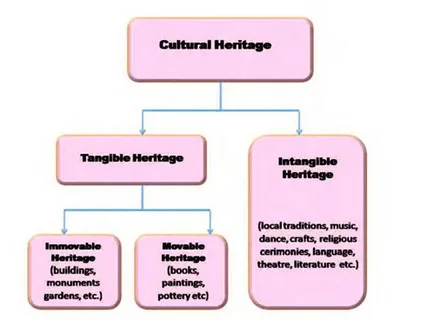
Cultural heritage plays a crucial role in connecting us to our past, grounding us in the present, and guiding future generations. Behind every successful preservation effort stands a cultural heritage advisor, whose expertise and insight ensure that valuable sites and traditions are conserved for years to come. Whether it’s advising developers on how to protect historical landmarks or working with Indigenous communities to safeguard sacred lands, cultural heritage advisors are indispensable in navigating the complexities of heritage management.
In this article, we will explore the essential role of a cultural heritage advisor, how they contribute to preserving cultural assets, and why their involvement is critical in various projects.
What Does a Cultural Heritage Advisor Do?
A cultural heritage advisor is a professional with specialized knowledge of historical, cultural, and archaeological assets. Their primary role is to provide expert advice on the conservation, protection, and management of cultural heritage resources. They collaborate with government bodies, developers, Indigenous groups, and other stakeholders to ensure that sites and artifacts of cultural significance are identified, documented, and preserved.
Some of the key responsibilities of a cultural heritage advisor include:
- Conducting Cultural Heritage Assessments: One of the first steps in any project involving land development is to determine whether the area holds any cultural or historical significance. A cultural heritage advisor will conduct detailed assessments to identify potential heritage sites or artifacts. This process is crucial to avoid damaging culturally important areas.
- Advising on Heritage Legislation: Heritage laws and regulations can be complex and vary by region. Cultural heritage advisors have in-depth knowledge of these legal frameworks and help project developers comply with all relevant laws. For example, in Australia, they must be well-versed in laws such as the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Heritage Protection Act 1984, which aims to protect Indigenous cultural heritage.
- Community Engagement: A cultural heritage advisor works closely with local communities, particularly Indigenous groups, to ensure that their voices are heard in decisions that affect their cultural heritage. This engagement often involves consultation meetings, site visits, and collaboration to develop management plans that reflect the community’s needs and values.
- Developing Heritage Management Plans: After assessing the heritage value of a site, a cultural heritage advisor works to develop a management plan. These plans provide guidelines on how to preserve the site while allowing for development or other land use activities. The plan typically outlines protective measures, such as buffer zones, or recommends mitigation strategies for potential impacts.
- Monitoring Development Projects: Once a management plan is in place, cultural heritage advisors often take on the role of monitoring projects to ensure that the heritage site is not compromised. They work with developers to implement mitigation measures, ensuring that the project progresses smoothly without damaging cultural assets.
Why Are Cultural Heritage Advisors Important?
The role of a cultural heritage advisor is critical for several reasons. First, they help protect sites that might otherwise be overlooked or destroyed. As urban development continues to expand, it is easy to forget the cultural or historical significance of an area. A cultural heritage advisor ensures that such sites are not lost in the process.
Second, they bridge the gap between stakeholders, including developers, governments, and communities. Developers may have economic interests in a project, while local communities may be concerned about preserving their cultural identity. A cultural heritage advisor facilitates dialogue and finds solutions that respect both parties’ interests.
Finally, cultural heritage advisors are essential in ensuring compliance with legislation. Developers who fail to take heritage into account may face legal consequences or project delays. By consulting a cultural heritage advisor early on, developers can avoid costly mistakes and ensure their projects meet all legal requirements.
How Cultural Heritage Advisors Protect Indigenous Heritage
Indigenous heritage is an integral part of cultural heritage and requires careful and respectful management. Indigenous communities often have a deep spiritual connection to the land, and certain sites may hold immense cultural and religious significance. Cultural heritage advisors play a crucial role in safeguarding these sites.
When working with Indigenous heritage, cultural heritage advisors focus on:
- Respecting Cultural Protocols: Advisors must engage with Indigenous communities in a respectful manner, adhering to cultural protocols. This means consulting Elders, obtaining permission to visit certain sites, and involving the community in decision-making processes.
- Protecting Sacred Sites: Sacred sites, such as burial grounds or ceremonial areas, are of immense importance to Indigenous communities. A cultural heritage advisor ensures that these sites are protected from development or other potentially harmful activities. In some cases, this may involve rerouting a project or creating a buffer zone around the site.
- Facilitating Knowledge Sharing: Cultural heritage advisors often act as intermediaries between Indigenous communities and developers or government bodies. They help facilitate knowledge sharing, ensuring that Indigenous cultural values are understood and respected by all stakeholders.
Challenges Faced by Cultural Heritage Advisors
While cultural heritage advisors play a vital role in preserving history, their work is not without challenges. Some of the common obstacles they face include:
- Balancing Development and Preservation: In many cases, developers are eager to move forward with their projects, which may lead to tension between economic interests and the need for preservation. Cultural heritage advisors must find ways to balance these competing priorities without compromising the integrity of heritage sites.
- Navigating Complex Legislation: Heritage legislation is often complicated, and different levels of government may have different requirements. Cultural heritage advisors must stay informed about the latest legal developments to ensure their advice is accurate and up-to-date.
- Gaining Community Trust: Cultural heritage advisors, especially when working with Indigenous communities, need to build trust. This can take time and requires a deep understanding of cultural values and protocols.
Why Developers Should Involve a Cultural Heritage Advisor Early
One of the most common mistakes developers make is waiting too long to consult a cultural heritage advisor. This can lead to significant delays if a heritage site is discovered during the construction phase. By involving a cultural heritage advisor early in the project, developers can avoid potential pitfalls and ensure that their project complies with all legal and cultural requirements.
Conclusion
The role of a cultural heritage advisor is crucial in preserving our past and ensuring that cultural and historical assets are protected for future generations. From conducting assessments to developing management plans and engaging with local communities, these professionals play a key role in navigating the complexities of heritage preservation. By understanding the value of a cultural heritage advisor, developers, governments, and communities can work together to strike a balance between development and conservation, ensuring that cultural heritage remains an integral part of our landscape.
If you’re planning a project that may impact cultural heritage, it’s essential to consult a qualified cultural heritage advisor to guide you through the process. Their expertise will help ensure that your project complies with all regulations and respects the cultural values of the communities involved.